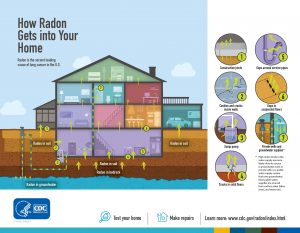
What is Radon?
Radon is a gas that one cannot smell, taste, or see. It is formed naturally when uranium, radium, and thorium break down in the rocks, soil, and groundwater and is then released into the air. Radon gas can be found outside and inside of buildings by getting through cracks and gaps in the walls and floors. The gas gradually builds up when inside and becomes harmful to one’s health over time.
Health Risk
Radon is the 2nd leading cause of lung cancer in the United States, following cigarette smoking. The combination of cigarette smoking and living in a home with high radon levels increases one’s risk of developing lung cancer exponentially.
The EPA estimates that radon causes about 21,000 lung cancer deaths each year across the nation. Of those, over 10% of deaths include people that have never smoked. The EPA also estimates that 1 in 15 homes within the US have high levels of radon that could lead to serious health issues, such as lung cancer.
Testing Radon Levels in Your Home
The EPA has determined that the average radon level is 4pCi/L (picocuries per liter). Any level greater than 4pCi/L poses a threat to one’s health and should be reduced. A home will not likely reach a radon level of 0pCi/L; however, any level of radon has some health risk associated, so it is still important to reduce radon to the lowest possible amount.
To know if there is a radon problem in your home, the first step is to conduct a radon test. A short-term radon test monitors the radon level in your home as quickly as in 2-7 days. To get a short-term test kit you can either request a free test kit through the Ohio Department of Health, buy a test kit online or hardware store, or hire a qualified tester to conduct a test for you. Another option is to purchase a long-term test kit that monitors radon levels in your home for at least 90 days. Long term tests often provide more reliable readings but take longer to complete. Long term tests may be purchased online or at some hardware stores.
If there presents to be a radon problem in your home, a radon mitigation system should be installed to lower the radon levels. These systems work by pulling the radon from the foundation of your home and then venting it outside. Contact a professional radon contractor for information on installing a radon mitigation system. To find radon testers and radon mitigation contractors, click here.
Tips on Radon Testing
When testing for radon, it is important to know under what conditions you will get the most accurate results:
Time of Year: Radon levels are at their highest level in colder conditions, which makes it better to test during the winter season. This is when windows and doors are typically closed tight for a long period of time, making the reading more accurate.
Weather: It is best to wait out any severe or unusual weather when testing for radon, as radon levels are affected by atmospheric pressure, precipitation, and temperature changes.
Location: Be sure to test the lowest level of the home that is used at least 10 hours a week.
Placement: When conducting the test, place the test kit at “breathing level” for the most accurate reading. It is best to keep the test kit away from the exterior walls, windows, and areas with a draft. Avoid testing in rooms with a high humidity (bathrooms, laundry room, kitchen, etc.).
Frequency: It is recommended by the EPA to test your home for radon at least once every two years. Tests may be completed more frequently. Radon detectors can also be used to signal high radon presence and may be purchased online or in some hardware stores.
If determining whether a radon mitigation system is necessary for your home, be sure to conduct at least two short term tests or a long term test to verify the test results are accurate readings. If further action is needed, contact a professional radon contractor for advice. To find radon testers and radon mitigation contractors, click here.
Ways to Reduce Radon Levels in Your Home
If your radon levels do not require a radon mitigation system (over 4pCi/L) but you would still like to see a reduction, there are other methods that you can do to lower amounts of radon in your home:
- Increase the air flow within your house by frequently opening your windows and running a fan.
- Seal the cracks in floors and walls with plaster, caulk, etc. 3. Invest in a cover for your sump pump.
- It is important to understand that these methods are not radon mitigation strategies, but methods to temporarily reduce radon presence in your home.
For more information on radon, visit the links below.
Links for More Information
EPA’s Citizen’s Guide to Radon
Links for Data
Links for Testing
ODH Request a Test Kit
Find Licensed Radon Testers and Radon Mitigation Contractors